Wondering how to determine if a URL is indexed by Google? Let’s explore the world of website visibility together.
As webmasters, we all want our pages to be recognized by this powerful search engine. Luckily, there are tools available to help us uncover the truth.
In this article, we will take a look at different options to check the URL indexing status in Google via Bulk Index Checker by CodeZy, Google Search Console, and other indexing tools.
So, let’s get started.
1. Bulk Index Checker
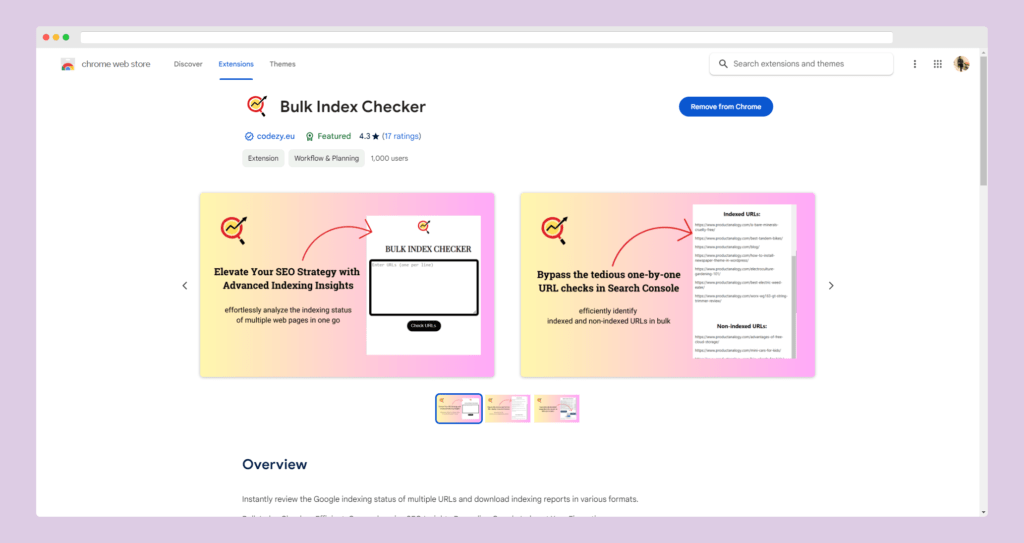
Bulk Index Checker is a free Chrome extension that allows users to check Google indexing status for multiple URLs with one request. It is a quick and efficient way to keep track of the indexing status for your URLs.
In comparison to GSC, the plus side of using Bulk Index Checker is that you don’t have to check the indexing status for each URL one by one. Similarly, if you usually use the “site:” parameter, you have to locate each URL individually. And if your website has more than 20 pages, the process becomes a bit hectic.
You can copy and paste a list of URLs (10 per request) and get the report for both indexed and non-indexed web pages right away.
2. Using Google Search Console to Check the Indexing Status
To check the indexing status of a URL, you can use Google Search Console. This tool allows you to monitor and analyze your website’s performance in Google Search.
To start, log into the Gmail account that manages your website’s profile and access Google Search Console.
Once you’re in, go to the left menu and click on ‘URL inspection.’ From there, you can enter the URL you want to check into the search field. Google Search Console will then show you the indexing status of that URL.
If the page is indexed, you’ll see the message ‘URL is on Google.’ This means that Google has successfully crawled and indexed your page, making it visible in search results. However, if the page isn’t indexed, the message will say ‘URL isn’t on Google.’ In this case, it’s important to investigate and address any issues that may be preventing Google from indexing your page.
To prompt Google to check the URL and test its indexability, you can click the ‘Request Indexing’ button. This will notify Google that you want them to crawl and index your page. Keep in mind that this process may take some time, so be patient and regularly check the indexing status.
In addition to Google Search Console, there are other tools available to check for indexed pages. For example, URL Profiler and ScrapeBox offer bulk options to analyze the indexing status of multiple URLs at once.
3. Verifying Indexing Status With Site: Search Command
Using the ‘site:’ search operator in Google followed by the URL allows you to quickly check if a specific page is indexed. This method provides a simple way to determine if Google has indexed a URL. Here’s how you can use the ‘site:’ search command to verify indexing:
- Enter ‘site:https://domain.com/example/’ in the Google search bar to see if a specific page is indexed.
- If the page appears in the search results, it means that it’s indexed by Google. If it doesn’t show up, the page isn’t indexed.
You can also use the ‘site:’ operator with just the domain or subdomain to check all indexed pages within that site. This broader search gives you a comprehensive view of which pages on your website have been indexed by Google.
Verifying indexing with the ‘site:’ search command is an efficient way to determine if your URL has been crawled and indexed by Google. By using this method, you can easily confirm the status of your page without the need to request indexing or wait for Google to discover it.
Troubleshooting Unindexed Pages and Next Steps
To troubleshoot unindexed pages and determine the next steps, it’s important to understand the various techniques and strategies available. Here are some steps to consider:
- Check if the page is indexed:
Start by using Google Search to check if a URL is indexed. Simply enter ‘site:example.com/page’ in the search bar, replacing ‘example.com/page’ with the actual URL you want to check. If the page appears in the search results, it’s indexed by Google.
- Use Google Search Console:
Import the URL into Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool to check its index status. If the page isn’t indexed, you can submit it for indexing through the console. Keep in mind that there’s a limit of 50 URLs per day for indexing.
Next steps to consider if a page isn’t indexed:
- Modify robots.txt:
Ensure that the robots.txt file allows Googlebot to crawl the page. Double-check for any disallow directives that might be preventing indexing.
- Use meta tags:
Implement appropriate meta tags such as ‘index’ and ‘follow’ to indicate that the page should be indexed and followed by search engines.
- Implement authentication:
If the page requires authentication to access, consider using authentication methods that allow search engine bots to bypass the authentication process for indexing purposes.


